Estuarine crabs such as those living in the leschenault inlet peel harvey estuary and swan river tend to move from estuaries into nearby marine waters during winter.
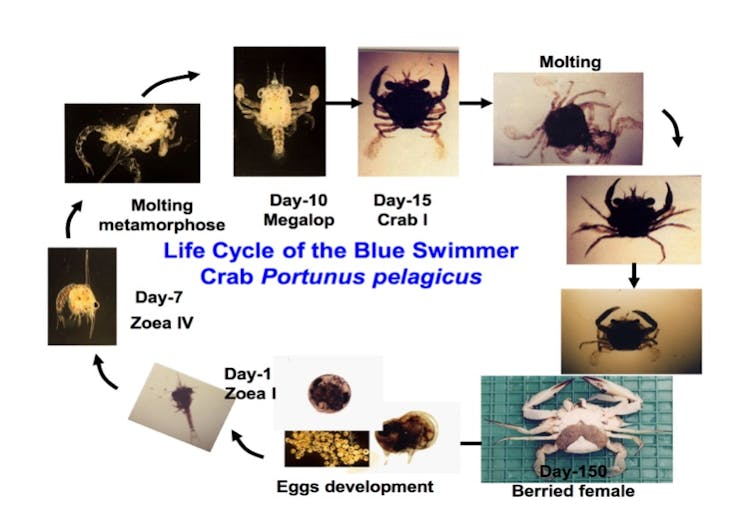
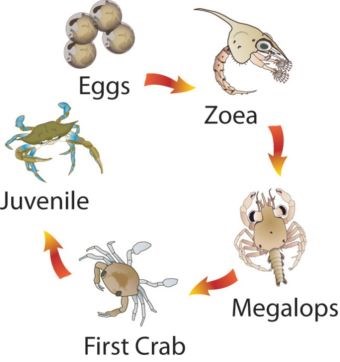
Blue swimmer crab life cycle.
The lifecycle of a blue swimmer crab credit.
Portunus armatus formerly portunus pelagicus also known as the flower crab blue crab blue swimmer crab blue manna crab or sand crab rajungan in indonesian and alimasag in tagalog kapampangan and pangasinan is a large crab found in the intertidal estuaries around most of australia and east to new caledonia.
Sapidus individuals exhibit sexual dimorphism.
Crabs from this family can usually be recognised by their flat disc shaped hind legs used as paddles for swimming.
Callinectes sapidus is a decapod crab of the swimming crab family portunidae.
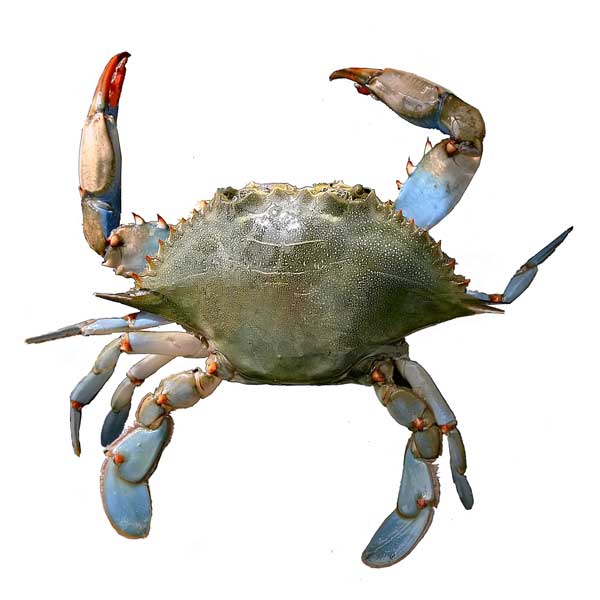
Blue swimmer crab.
Blue swimmer crabs are large crabs native to the indian and pacific ocean and the middle east coast of the mediterranean.
They float on the surface of the water far from the coastline.
Pelagicus are a tropical species and belong to the portunidae family.
Female blue crabs mate only once in their lives when they become sexually mature immediately following their pubertal molt immediately following this molt the female is known as a sook when approaching this pubertal molt females release a pheromone in their urine which attracts males.
Male blue swimmer crabs are blue with white spots and female crabs are a dull green brown.
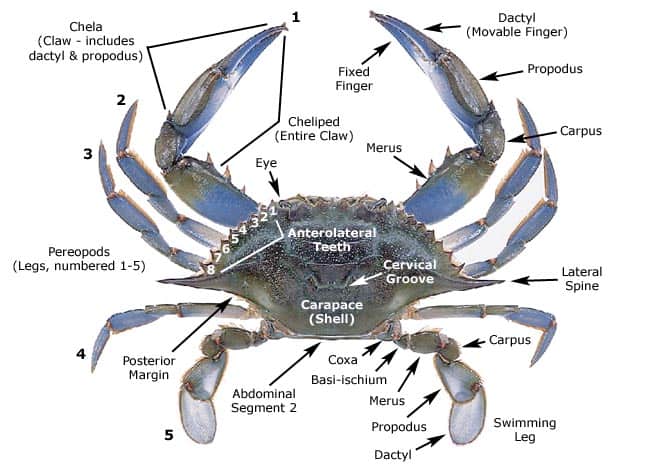
The genus callinectes is distinguished from other portunid crabs by the lack of an internal spine on the carpus the middle segment of the claw as well as by the t shape of the male abdomen.
Facts habitat and life cycle explanation.
The family also includes other large edible crabs found in australia such as mud crabs.
The blue crab s mating season occurs between may and october.
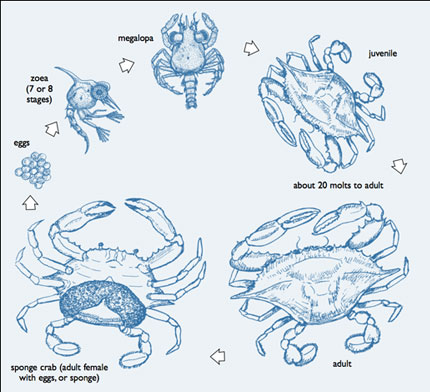
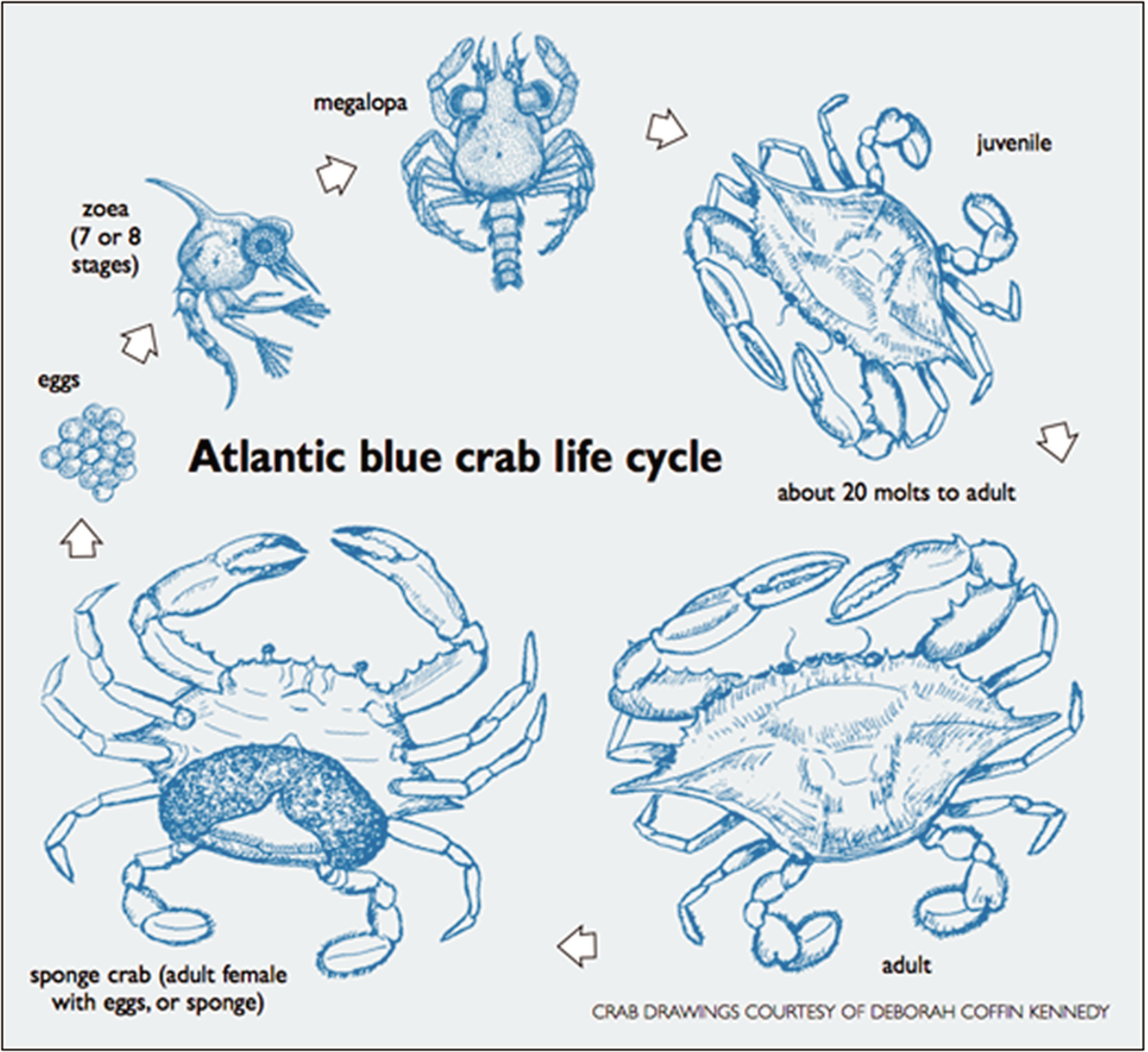
Blue crab life cycle.
The main body or carapace of blue swimmer crabs can grow up to 25 cm 9 8 inches in width.
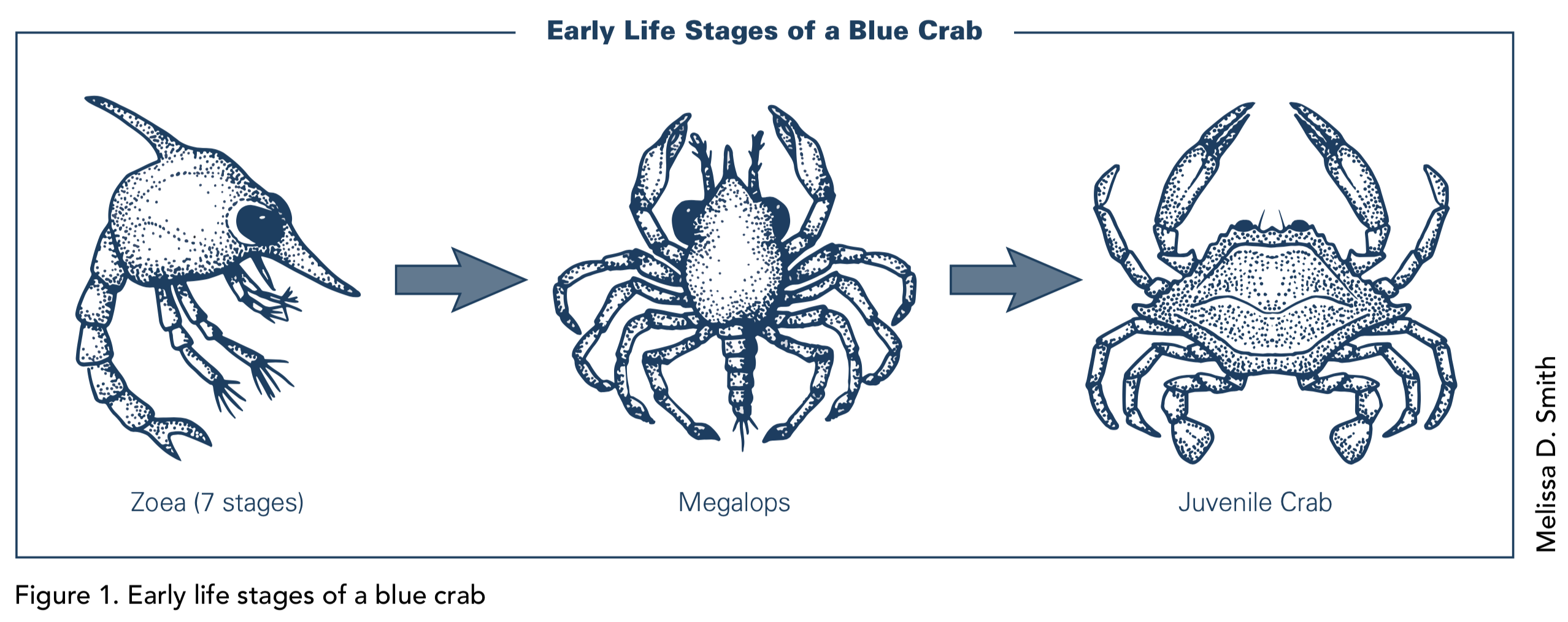
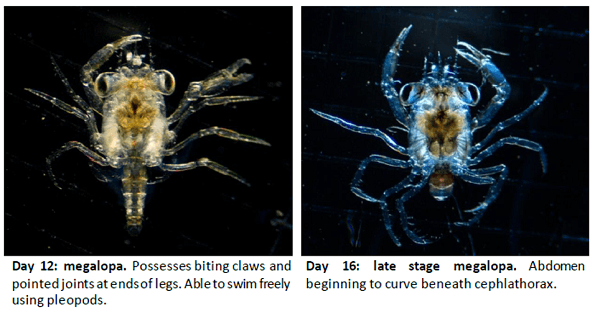
Zoea zo ee ya blue swimmer crabs hatch from their eggs in early summer as tiny larvae known as zoea.
A male will mate with a female after she has completed her final molt and she has a soft shell.
During her adult life the female blue crab remains in the estuary although usually in higher salinity water than males she eats fish crustaceans worms and mollusks and may be preyed upon by large fish birds and mammals including humans her molting rate increases during warmer months although water temperatures greater than 30 o c 86 o f appear to inhibit molting.
Blue swimmer crabs portunus armatus.
Their back legs are smaller sized and shaped like paddles making them powerful swimmers.
The female will lay up to two million eggs in a spongy mass that starts off an orange color but gets closer to black as it comes time for the crabs to hatch.
Page 2 of 4 life cycle the timing and movements of blue swimmer crabs vary between locations.
Blue swimmer complainers have actually sizable face lower legs that they make use of for both hunting and also self defense.